Background on train delays
Train delays have been increasing in the past few years in terms of the numbers of delays and the amount of delay.
A train could be delayed due to many factors - once the primary (first) delay happens to the first train, that train can have knock-on effects on other trains, causing them to be delayed. These subsequent delays are called reactionary delays.
Over time, the amount of primary delays have remained relatively stable, but reactionary delays have risen considerably. This has resulted in a continuous deterioration of network performance, which is measured by the Public Performance Measure (PPM) statistic.
Although it would be ideal to reduce or prevent the primary delays as much as possible in the first place, the various causes are out of the rail industry's control (e.g. bad weather or random incidents such as trespassers). It is therefore difficult to reduce or prevent primary delays which may explain why primary delays have stayed stable. Consequently, it is more feasible to reduce or prevent reactionary delays. However, current systems are unfortunately unable to predict and manage reactionary delays accurately and effectively.
Given that the rail industry has been collecting large amounts of various data related to train operations, a logical approach is to apply modern artificial intelligence and machine learning techniques to explore exploiting this data to discover knowledge useful for improving network performance.
However, there are two basic challenges. The first is that rail related datasets are complex, diverse and stored in silos, making it a challenge to collate and integrate all the relevant data into a meaningful representation for further analysis. The second challenge is how to efficiently extract useful knowledge from this data and then use it to effectively assist Train Operation Companies (TOC) in making evidence-based decisions for improving their services.
In our study, we take on these challenges and aim to develop an intelligence ensemble system for predicting reactionary delays and then make suggestions for reducing and/or preventing further delays.
Therefore this feasibility study proposes to investigate how to use artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies to address the aforementioned challenge with the ultimate aim of developing an intelligent system for predicting and preventing reactionary delays. The following sections detail the scope of this study, a preliminary design of an Artificial Intelligence enhanced decision support system (AIEDSS) for network operators, and the associated tasks and deliverables.
Aim and Objectives of the Study
The aim of this research is to study the feasibility of developing an intelligence ensemble system for predicting and preventing reactionary delays, with the following primary objectives.
- To analyse existing datasets relevant to train operations to discover patterns of train delays and to quantify the salience of the relevant factors.
- To apply machine learning ensemble approaches to the existing data to automatically generate machine learned intelligence models.
- To build a prototype of an intelligence ensemble system and to evaluate its feasibility using one or two models of lines of train services as the basis for use cases.
The Intelligence Ensemble System
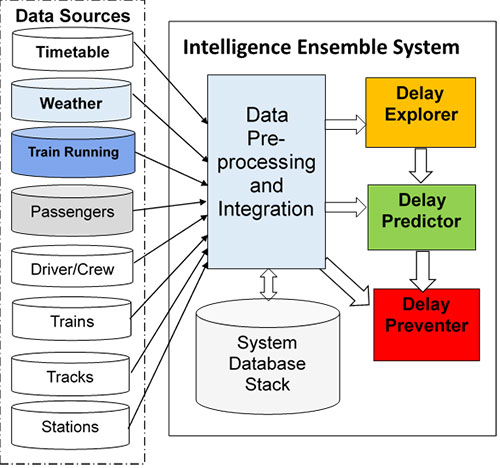
The proposed intelligence ensemble system, as shown in the figure below, consists of four key functional modules: data pre-processing and integration (and database), Delay Explorer, Delay Predictor, and Delay Preventer.
The project has gone very well so far. A large amount of railway related data (from 13 different sources) has been collected, cleaned and processed - this includes real time running data, historical performance data, data about incidents where trains were delayed, and weather data for the past two years. After evaluating the necessary requirements and the feasibility of the system, the basic components of the intelligence ensemble system are currently being prototyped.
Contact us
School Of Computing Sciences
University of East Anglia
Norwich Research Park
Norwich
NR4 7TJ
Related Links

)