Novel tools for reducing bias in Next Gen Sequencing
A novel, simple, yet robust solution to overcome cloning bias in sRNA libraries. The tools could be easily incorporated into existing sRNA cloning kits with minimum costs and are readily available for use.
Advantages
doubles sequence coverage; compared to Illumina protocols there is an increase in sequencing coverage by up to 100%
gives more quantitative result that reflects better the true sRNA pool in the sample
identifies previously un-cloned sequences.
Small RNAs (sRNAs) are key regulators of genetic activity and accurate representation of sRNA in sequencing experiments is critical to the interpretation of biological data. Next generation sequencing (NGS) is now the gold standard for profiling sRNA and discovering new RNA. Further, NGS based approaches have now been extended to the study of protein function too. With such a heavy reliance on NGS, it is essential that the tools and protocols used in NGS generate accurate and reliable sequence data.
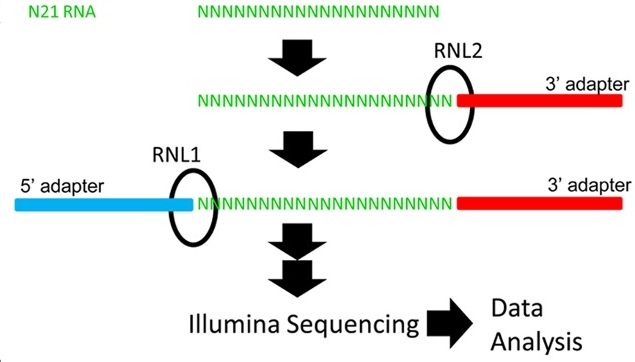
RNA ligases are essential in creating cDNA libraries prior to NGS sequencing. However, a number of recent publications reported that RNA ligases used in cDNA preparation actually mediate sequence specific ligation and the NGS approaches using these RNA ligases therefore do not represent all sRNA present in biological samples. The cause for sequence specific ligation is that the ligases preferentially ligate ends to each other that have more chance to be close to each other. This means that sRNAs that can efficiently anneal to the adapters have a higher chance to be ligated.
Professor Tamas Dalmay, a renowned expert in siRNA biology from the School of Biological Sciences has developed a novel, simple, yet robust solution to overcome this problem. Dalmay and colleagues have developed a set of adapters that contain degenerated nucleotides therefore they are a pool of many sequences instead of one fixed sequence. Consequently, they give a chance to increase the different sRNAs that form a stable duplex, leading to better coverage and more quantitative libraries.
Publications
Silence, 2012, 3(1):4. doi:10.1186/1758-907X-3-4
Patents
Patents granted in Europe EP2737086 B1, Singapore SG11201403667V and a patent application in the US US2014243213 A1.
Principal Investigator
Team led by Professor Tamas Dalmay
Further Details
For more information on this licensing opportunity, please contact the IP Office.
:focus(1352x1011:1353x1012))